Electric Vehicles and Alternative Fuels
Electric vehicles (EV) and other alternative fuels — including compressed natural gas (CNG), liquified natural gas (LNG), propane, and hydrogen — are playing an increasingly important role in Pennsylvania's transportation network. To meet public and industry expectations and ensure Pennsylvanians can get to their destinations safely and reliably using EVs and alternative fuels, PennDOT is planning for the new infrastructure needed to support this transition today — paving the way for the cleaner, more energy-efficient travel of the future.
PennDOT is actively collaborating with federal, state, and local partners to expand the Commonwealth's EV charging and alternative fuels network. Through the Federal Highway Administration's (FHWA) Alternative Fuels Corridor (AFC) program, the department is proactively planning for the build-out of fast-charging EV and alternative fuel stations, particularly along highways, to support the needs of drivers for reliable long-range and employment-related travel. PennDOT also works closely with the
Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection (PA DEP), which leads a number of EV and alternative fuels initiatives and funding programs.
More information on EVs, the status of Pennsylvania's EV charging network, the AFC program, and other departmental efforts regarding alternative fuels may be found below.
Understanding the Basics of EVs and Charging Infrastructure
Types of Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Charging Stations
There are three main types of EVs:
- Hybrid EVs
- Plug-in hybrid EVs
- All-electric EVs, also known as battery EVs (BEVs)
PennDOT's EV planning is focused on supporting drivers of all-electric BEVs, which do not have the option of fueling with gasoline, by developing a safe and reliable network of publicly accessible EV charging stations statewide.
| EV Type | Gas Tank | Electricity Port | Charging Type |
|---|
| Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) | Yes | No | No plug; Charged through regenerative braking |
| Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) | Yes | Yes | Plug-in: Level 1, Level 2 |
| Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) | No | Yes | Plug-in: Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast |
For more information on the differences between HEVs, PHEVs, and BEVs, please visit the
Alternative Fuels Data Center Hybrid and Plug-In Electric Vehicles resource page.
Types of EV Charging Infrastructure
There are three levels of EV charging for plug-in EVs (PHEVs and BEVs):
- Level 1
- Level 2
- DC Fast
PennDOT's EV charging station planning is mostly focused on
DC Fast stations, which can charge an EV in just
20-30 minutes — or about the same amount of time it takes to stop for a quick meal on the highway.
| Plug-In EV Charging Type | Range | Use
| Connector Type |
|---|
Level 1
| 3.5-6.5 miles per 1 hour charging | Residential parking, such as home garage |
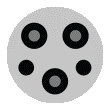 J1772
J1772
 Tesla Tesla |
Level 2
| 14-35 miles per 1 hour charging | Public or private parking for several hours, such as at a workplace, hotel, shopping center, entertainment event, or residence |
 J1772
J1772
 Tesla Tesla |
DC Fast (Level 3)
| 200 miles per hour charging (or more for newer models) | - For a quick stop on a long-distance trip, such as in the parking area of a gas/convenience store, restaurant, or shopping center
- For use by drivers who lack access to home-charging, such as in metropolitan areas
|
 CHAdeMO
CHAdeMO
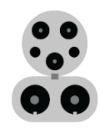 CCS
CCS
 Tesla Tesla |
For more information on the differences between charging infrastructure levels, please visit the
Alternative Fuels Data Center Charging Infrastructure resource page.
Pennsylvania's Fast-Charging Network
For EVs to be as convenient as traditional cars (and of course, much cleaner!), drivers need to feel confident that they will be able to find a public DC fast-charging station on the road when they need to recharge mid-trip. With the U.S. Department of Transportation setting a goal to build a network of half a million fast-charging stations nationwide by 2030, including $5 billion in formula funding to the states,
the opportunity is now for PennDOT to play its part in making it as convenient as possible to drive an all-electric vehicle in the Commonwealth, for all types of trips.
Electric Vehicle Registrations
The following map displays electric vehicle registrations in Pennsylvania by county and by zip code. This data is updated quarterly and may be downloaded in a table format when viewing the larger map.